Current Pediatric Research
International Journal of Pediatrics
Methodology used for collecting saliva of preterm newborns to measure cortisol: Systematic review
1 PhD Student, Child and Adolescent Health, Department of Pediatrics, Faculty of Medical Sciences, University of Campinas, UNICAMP, São Paulo, Brazil
2Assistant Professor, Division of Neonatology, Department of Pediatrics, Faculty of Medical Sciences, University of Campinas, UNICAMP, São Paulo, Brazil.
3Deparment of Pathology, Medical Science School, University of Campinas, UNICAMP, São Paulo, Brazil.
4Professor, Pediatrics Neonatal Section, Department of Pediatrics, University of Campinas, UNICAMP, Sao Paulo, Brazil.
- *Corresponding Author:
- Vanessa Carina Pepino Stelini
Rua Adolfo Barbalho de Uchoa Cavalcanti
131, casa 24, cep: 13092-200. Jardim Lumen Christ
Campinas-SP
Brazil.
Tel: 55 19 9 96481049
E-mail: vanpepino@yahoo.com
Accepted date: June 05, 2017
Objective: Systematically analyze the methods used by clinical trials published in the last 10 years to collect preterm newborn saliva to measure cortisol. Method: Three databases PubMed, Scopus and Embase were searched in December 2016. Two researchers independently selected studies by title, and the abstracts of the selected studies were read to determine which ones met the inclusion criteria. All clinical trials of hospitalized preterm newborns that collected saliva to measure salivary cortisol were included. Results: Two types of methods were used for collecting saliva: aspiration or absorption, using absorbent materials. All nine aspiration-based studies and the 24 absorptionbased studies managed to measure salivary cortisol in at least some samples. Twenty-one studies reported losing some samples. The most common reasons for sample losses were insufficient saliva. Meta-regression (meta-analysis) and random effects model investigated possible relationships between percentage of sample losses and the following variables at a significance level of 5%: collection method, collection material, collection time and type of assay. Aspiration resulted in fewer sample losses than absorption (p<0.0001). However, only 33.3% (3 of 9) of aspiration-based studies reported the number of sample losses against 81.8% (18 of 22) of absorption-based studies. The most used assays to measure salivary cortisol were ELISA and radioimmunoassay. Conclusion: Salivary cortisol measurement in preterm newborns may be useful for assessing and comparing the level of stress generated or relieved by different stimuli. Saliva collection methods have not been standardized, preventing the reproduction of studies that use these methods.
Keywords
Salivary cortisol, Preterm, newborn.
Introduction
Although the inherent care provided by a neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) stresses preterm newborns (PTNs), it is critical for their survival [1]. Studies have searched for alternative and complementary therapies, such as music therapy, tactile-kinesthetic stimulation, kangaroo care, and skin-to-skin contact, to the standard treatment to reduce factors that cause tension in an NICU [2-5]. Salivary cortisol level, which can be detected already in the first week of life, increases in individuals experiencing adverse situations, and PTNs have higher salivary cortisol level than term newborns [6,7]. In order to assess the efficacy of alternative and complementary therapies, noninvasive tests, such as PTN salivary cortisol measurement, have been performed [8-12]. Noninvasive methods that measure cortisol to possibly determine newborns’ level of discomfort may be used to assess routine and new NICU procedures.
Despite the possible benefits of this type of assessment in newborns, studies discuss whether salivary cortisol is indeed associated with newborn’s stress and plasma cortisol levels [13,14]. Studies that performed salivary cortisol measurements used different methodologies. The objective of this review was to systematically analyze the methods used by clinical trials published in the last 10 years to collect PTNs’ saliva to measure cortisol, to determine the most successful methods for collecting saliva and to list the advantages and disadvantages of each method.
Method
Three databases, PubMed (United States National Library of Medicine of the National Institutes of Health), Scopus, and Embase (Excerpta Medica Database) were searched in December 2016 using the keywords “salivary cortisol” AND “premature.” This was the combination of keywords that returned the highest number of studies in each database.
A database was created using the software EndNote, which manages references, and the data were judiciously stored in folders. Two researchers independently selected studies by title and the abstracts of the selected studies were read to determine which ones met the inclusion criteria. If the researchers disagreed, the study was saved to be read in full.
Selection Criteria
All studies found in the abovementioned databases that collected saliva from PTNs were selected.
Inclusion Criteria
All clinical trials of hospitalized PTNs that collected saliva to measure salivary cortisol published in the last 10 years in Portuguese, English or Spanish were included.
Exclusion Criteria
Studies that collected saliva after the newborn left the hospital, posters, studies that measured cortisol in term newborns, and studies in languages other than those mentioned above were excluded.
Results
The keywords “salivary cortisol” AND “premature” returned 235 studies, 86 from PubMed, 69 from Embase and 80 from Scopus. Repeated studies were eliminated, resulting in 152 studies for title assessment. Two researchers performed all inclusion and exclusion procedures independently.
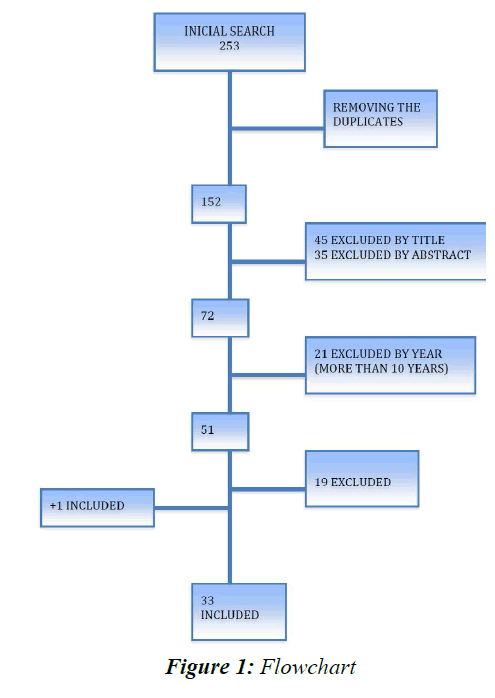
Forty-five articles were excluded based on their titles, and later, another 35 studies were excluded based on their abstracts. Twenty-one studies of the remaining 72 were excluded because they had been published before December 2006. Thus, 51 studies were read in full, of which 32 complied with the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Nineteen studies were eliminated during this phase for the following reasons: five did not collect saliva during hospital stay, four did not collect saliva from PTNs, two did not measure salivary cortisol, only plasma cortisol, three were presented as posters, two only collected maternal saliva (n=2), one was published in Persian, and the whole text of two was not found (Figure 1) [15-33]. One more study listed in the references of one of the reviewed studies was included [13]. In summary, 235 articles were found in the three researched databases, and after elimination of the duplicates and application of the inclusion and exclusion criteria, 33 studies remained (Table 1).
| Autor/Ano | Title | Objectives |
|---|---|---|
| Soliman et al. 2016 [8] | Does Topical Lidocaine Reduce the Pain Associated With the Insertion of Nasal Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Prongs in Preterm Infants? A Randomized, Controlled Pilot Trial | To evaluate the efficacy of topical lidocaine 2% gel in reducing the pain associated with the insertion of nasal continuous positive airway pressure (nCPAP) prongs in preterm infants |
| Â Castral et al. 2015 [9] | Maternal mood and concordant maternal and infant salivary cortisol during heel lance while in kangaroo care | To examine the concordance of salivary cortisol reactivity between 42 mothers and their stable preterm infants during routine infant heel lance while in KC and to compare salivary cortisol between groups of mothers with and without PPDA and their infants |
| Moore et al. 2015 [10] | Comparison of cortisol samples in the first two weeks of life in preterm infants | To examine cortisol samples for usability, associations, and individual stability in neonates |
| Osman et al. 2015 [11] | Assessment of pain during application of nasal-continuous positive airway pressure and heated, humidified high-flow nasal cannula in preterm infants | To assess pain and its severity in preterm infants during application of nCPAP and HHHFNC |
| Schwilling et al. 2015 [12] | Live music reduces stress levels in very low-birth weight infants | To evaluate the effect of live harp music on the stress level indicators of preterm infants in a neonatal intensive care unit |
| Â Badiee et al. 2014 [34] | Co-bedding of twin premature infants: calming effects on pain responses | To evaluate the effect of live harp music on the stress level indicators of preterm infants in a neonatal intensive care unit |
| Campbell-Yeo et al. 2014 [41] | Co-bedding between preterm twins attenuates stress response after heel lance results of a randomized trial  | To determine whether co-bedding of preterm twins has analgesic effects during heel lancing or not |
| Candia et al. 2014 [35] | Influence of prone positioning on premature newborn infant stress assessed by means of salivary cortisol measurement: Pilot study | To examine the effect of co-bedding between preterm twins on stress response after heel lance |
| Dorn et al. 2014 [42] | Influence of acoustic stimulation on the circadian and ultradian rhythm of premature infants | To assess the influence of prone positioning on the stress of newborn premature infants through the measurement of the salivary cortisol concentration and the evaluation of physiological and behavioral responses before and after changes in body positioning |
| Klingenberg et al. 2014 [43] | Patient comfort during treatment with heated humidified high flow nasal cannula versus nasal continuous positive airway pressure: A randomised cross-over trial | To evaluate the development of the circadian rhythm of the salivary cortisol in premature infants and its correlation with the onset of the sleep?activity behavior pattern during the first 3 weeks of life under controlled light:dark conditions. Furthermore, we investigated the influence of acoustic stimulation by audiotaped lullabies or the maternal voice on the cortisol values and long-term sleep activity patterns |
| Neu et al. 2014 [55] | Effect of holding on co-regulation in preterm infants: A randomized controlled trial | To determine whether kangaroo holding of healthy preterm infants over the first eight weeks of an infant's life facilitates co-regulation of salivary cortisol between mother and infant |
| Maas et al. 2014 [14] | Relationship of salivary and plasma cortisol levels in preterm infants: Results of a prospective observational study and systematic review of the literature | To investigate the relationship of salivary and plasma cortisol levels in preterm infants with special regard to usability of salivary cortisol in diagnostic work- up of infants at risk of adrenal insufficiency |
| Badiee et al. 2013 [36] | The calming effect of maternal breast milk odor on premature infants | To compare the effectiveness of maternal breast milk odor and formula milk odor in soothing premature infants undergoing heel lancing |
| Cabral et al. 2013 [39] | Measurement of salivary cortisol as a marker of stress in newborns in a neonatal intensive care unit | To evaluate the newborn stress response during the inpatient time in the NICU |
| Mitchell et al. 2013 [44] | Does daily kangaroo care provide sustained pain and stress relief in preterm infants? | To determine whether stress in preterm infants, measured with salivary cortisol, decreases after five days of KC compared to five days of SC |
| Moore et al. Â 2013 [45] | Relations between feeding intolerance and stress biomarkers in preterm infants | To examined feed Intolerance as a stress-related disease involving brain-gut interactions and tested the model of allostatic load and complications of prematurity |
| Ng et al. 2013 [46] | A novel method of collection of saliva for estimation of steroid levels in extremely premature infants | To describe a simple, non-stressful way to obtain saliva samples for cortisol dosing in premature infants |
| Ribeiro et al. Â 2013 [38] | Human milk for neonatal pain relief during ophthalmoscopy | To establish the effectiveness of human milk, compared with sucrose for pain relief in premature infants subjected to ophthalmoscopy for early diagnosis |
| Mitchell et al. 2012 [13] | Challenges, guidelines and systematic review of salivary cortisol research in preterm infants | To determine the feasibility of collecting saliva from neonates in moderate respiratory distress who were between 27 and 30 weeks gestational age |
| Castral et al. 2012 [58] | Maternal factors regulating preterm infants' responses to pain and stress while in maternal kangaroo care | To investigate the association between maternal factors (behavior, depression and/or anxiety and stress) and the response of newborns to pain and stress when undergoing heel puncture for the neonatal screening test while held in the kC |
| Ivars et al. 2012 [47] | Nasopharyngeal suctioning does not produce a salivary cortisol reaction in preterm infants | To investigate whether NPS is stressful in CPAP-treated preterm infants and in full-term infants. The primary outcome was salivary cortisol reactivity |
|  Mo¨relius et al. 2012 [48] | The Stockholm Neonatal Family-Centered Care Study: Effects on salivary cortisol in infants and their mothers | To evaluate the effect of family-centered care on salivary cortisol reactivity in mothers and preterm infants and the correlation between them |
| Â Chou et al. 2011 [49] | The relationship of salivary and cord blood cortisol in preterm infants | To explore the use of salivary cortisol as an accurate measure of adrenal steroid production in premature infants, correlation between salivary and serum cortisol in premature infants looms as a possible alternative |
| Cong et al. 2011 [50] | Randomized crossover trial of kangaroo care to reduce biobehavioral pain responses in preterm infants: A pilot study |
To determine whether KC reduced heel stick pain as measured by the PIPP and salivary and serum cor- tisol levels better than the standard incubator care in two studies when KC was administered for 80 or 30 min before the heel stick |
| Bauer et al. 2009 [40] | Effects of budesonide inhalation on energy expenditure, somatic growth and salivary cortisol levels in preterm infants with chronic lung disease |
To investigate the impact of inhaled glucocorticoids on EE, somatic growth and adrenal function in preterm infants with CLD |
| Cignacco et al. 2009 [51] | Variability in pain response to a non-pharmacological intervention across repeated routine pain exposure in preterm infants: a feasibility study | The purpose of the present study was to investigate the impact of inhaled glucocorticoids on EE, somatic growth and adrenal function in preterm infants with CLD |
| Neu et al. 2009 [56] | Coregulation in salivary cortisol during maternal holding of premature infants | Â To examine co-regulation between mothers and preterm infants in HPA activity, as indicated by salivary cortisol levels, while mothers held their infants |
| Schaffer et al. 2009 [52] | Antenatal betamethasone administration alters stress physiology in healthy neonates | To analyze hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis balance in healthy newborns after antenatal beta-methasone treatment for lung maturation where delivery could be prolonged until or near term |
| Gibbins et al. 2008 [37] | Pain behaviours in extremely low gestational age infants | To examine the physiological, behavioural and biochemical responses to painful and non-painful procedures in ELGA infants and the influence of gestacional age and sex |
| Kleberg et al. 2008 [53] | Lower stress responses after newborn individualized developmental care and assessment program care during eye screening examinations for retinopathy of prematurity: A randomized study | To investigate whether a NICAP during a retinopathy of prematurity examination results in less adverse behavioral, pain and stress responses as compared with standard care |
| Davis et al. 2006 [54] | Antenatal betamethasone treatment has a persisting influence on infant HPA axis regulation | To examine the consequences of antenatal betamethasone exposure on postnatal stress regulation |
| Morelius et al. 2006 [59] | Is a nappy change stressful to neonates? | To investigate whether NICU infants have different pattern of stress and pain responses than healthy newborns when challenged by a non-painful everyday care routine |
| Ashwood et al. 2006 [57] | Neonatal adrenal function after repeat dose prenatal corticosteroids: A randomized controlled trial | Do repeat prenatal corticosteroids suppress neonatal cortisol concentrations? |
CPAP: Nasal-Continuous Positive Airway Pressure; HL: Heel Lancer; PPDA: Post-Partum Depression and/or Anxiety ; HHHFNC: Humidified High-Flow Nasal Cannulae; NICU: Neontal Unit Care; NPS: Nasopharyngeal Suctioning; KC: kangoroo Care; HPA: Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenocortical; ELGA: Extremily Low Gestacional Age; NIDCAP: Newborn Individualized Developmental Care and Assessment Program; CLD: Chronic Lung Disease
Table 1. Description of study objectives.
Two types of methods were used for collecting PTNs’ saliva: aspiration or absorption, using absorbent materials. Aspiration was performed with a pipette, syringe connected to a plastic tube, needleless push button blood collection set or probe or tracheal suction set [8,9,11,34-40]. The absorbent materials used for absorbing the newborns’ saliva were swabs or cotton buds of different brands and models, filter paper or sterile dental cotton roll tied with a dental floss [6,10-14,37,41-57]. One of the studies used both collection methods, swab and aspiration and one did not specify how PTN saliva was collected [37,58].
Only one of the studies that specified saliva extraction method did not use centrifugation. That study collected saliva with a sterile dental cotton roll and extracted the saliva by placing the roll inside a 5 ml syringe and pressing the plunger to expel the saliva [57].
Collection time varied between studies. Aspiration-based studies did not inform the duration of the procedure, and only two studies reported the amount of collected saliva [35,39]. Aspiration pressure was not informed by any study, and only one study reported using “enough negative pressure to suck 0.5 to 1.0 ml of newborn saliva” [38]. Nine absorption-based studies did not inform for how long the absorbent material stayed in the newborn’s mouths [2,6,10,14,37,41,47,48,53]. Four studies that provided such information left the material in the newborns’ mouths for 5 min [45,50,52,54]; one, for 10 min [43]; one, for at least 20 min [51]; one, for 5 to 10 min [42]; one, for 20 to 25 min [44]; one, for 1 to 2 min [46]; one, for 30 to 60 s [49]; and one left the first 10 samples in the PTNs’ mouths for 3 min and the subsequent 53 samples, for 20 min [13].
All nine aspiration-based studies and the 24 absorptionbased studies managed to measure salivary cortisol in at least some samples. Two studies omitted the results because their samples did not have enough saliva [37,43].
Twenty-one studies reported losing some samples [6,8,10-14,35,37,41-46,48,51,53,55-57]. The most common reasons for sample losses were insufficient saliva and/or contamination with blood [6,8,10-14,37,41- 46,48,51,53,55-57]. Only one study lost samples due to the viscosity of the absorbent material [35]. The percentage of sample losses due to insufficient saliva ranged from 0% to 90%. Of the studies that specified collection method and reported the total number of sample losses, three used aspiration and 18 used absorbent materials. Six aspirationbased studies and four absorption-based studies did not inform whether any samples were lost or the number of sample losses (Table 2).
| Author/Year | Collection Method | Material Used | Collection Time | Assay | % of Samples Lost | Total Number of Samples |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soliman et al. 2016 [8] | Aspiration | 500 µl pipette | - | ELISA | 11.66% | 60 |
| Castral et al. 2015 [9] | Aspiration | Plastic tube connected to needleless syringe | - | RIE | - | - |
| Moore et al. 2015 [10] | Absorbent material | Pediatric swab | 5 min | RIE | 14.13% | 93 |
| Osman et al. 2015 [11] | Aspiration | 500 µl pipette | - | ELISA | 10.12% | 79 |
| Schwilling 2015 et al. [12] | Absorbent material | Swab split in 4 | - | 2D-LC-MS/MS | 8.88% | 180 |
| Badiee et al. 2014 [34] | Aspiration | 2 ml syringe | - | ELISA | - | 200 |
| Campbell et al. 2014 [41] | Absorbent material | Swab | - | ELISA | 26.67% | 129 |
| Candia et al. 2014 [35] | Aspiration | 10 ml syringe connected to a needleless flexible intravenous catheter (18) | - | ECL | 23.80% | 42 |
| Dorn et al. 2014 [42] | Absorbent material | Swab | 5 to 10 min | ELISA | 35% | 422 |
| Klingenberg et al. 2014 [43] | Absorbent material | Swab | 10 min | RIE | 86.25% | 80 |
| Neu 2014 [55] | Absorbent material | Filter paper | 30 s to 2 min | ELISA | 3.8% | 711 |
| Maas et al. 2014 [14] | Absorbent material | Eye sponge | - | ELISA | 48.27% | 58 |
| Badiee et al. 2013 [36] | Aspiration | 2 ml syringe | - | ELISA | - | 100 |
| Cabral et al. 2013 [39] | Aspiration | Aspiration probe no. 4 Levine and a 5 ml syringe | - | RIE | - | 40 |
| Mitchell et al. 2013 [44] | Absorbent material | Eye sponge | 3 min first 10 samples and 20 min the next 53 samples | ELISA | 36.84% | 76 |
| Moore et al. 2013 [45] | Absorbent material | Pediatric swab | 5 min | ELISA | 13.98% | 93 |
| Ng et al. 2013 [46] | Absorbent material | Swab | 1 to 2 min | ELISA | 15% | 195 |
| Ribeiro et al. 2013 [58] | Aspiration | Needleless push button blood collection set no. 21 connected to a 3 ml syringe | - | RIE | - | - |
| Mitchell et al. 2012 [13] | Absorbent material | Filter paper | 10 samples for 3 min 53 samples for 20 min |
ELISA | 3 min=70% 20 min=17% | 3 min=10 20 min=53 |
| Castral et al. 2012 [58] | Does not specify | - | - | - | - | - |
| Ivars et al. 2012 [47] | Absorbent material | Cotton buds | - | RIE | 0% | 44 |
| Morelius et al. 2012 [48] | Absorbent material | Cotton buds | - | RIE | 15.916% | 578 |
| Chou et al. 2011 [49] | Absorbent material | Cotton swab split in 2 | 30 to 60 s | RIE | - | - |
| Cong et al. 2011 [50] | Absorbent material | Swab | 4 to 5 min | RIE | - | - |
| Bauer et al. 2009 [40] | Aspiration | Tracheal suction set | - | - | - | - |
| Cignacco et al. 2009 [50] | Absorbent material | Oral Swab | 20 min | RIE | 1.11% | 90 |
| Neu et al. 2009 [56] | Absorbent material | Filter paper folded in half | 30 s to 3 min | ELISA | 5% | 40 |
| Schaffer et al. 2009 [52] | Absorbent material | Swab | 5 min | EMCL | - | - |
| Gibbins et al. 2008 [37] | Absorbent material+Aspiration | Swab Qtip and aspiration with syringe | - | RIE | 90% | 40 |
| Kleberg et al. 2008 [53] | Absorbent material | Cotton bud | - | RIE | 25% | 310 |
| Davis et al. 2006 [54] | Absorbent material | Swab Qtip | 5 min | DELFIA | - | - |
| Morelius 2006 [59] | Absorbent material | Cotton buds | - | RIE | Diaper change 1:15.4% Diaper change 2:18% |
78 |
| Ashwood 2006 | Absorbent material | Dental cotton roll tied by dental floss | 10 to 20 min | ELISA | 15% | 320 |
Table 2. Description of collection method, material, assay and % of sample lost.
This group of studies (three that used aspiration and 18 that used absorbent materials) made 181 and 3560 attempts to collect saliva using aspiration and absorbent materials, respectively. Aspiration-based studies lost fewer samples than absorption-based studies, regardless of assay method. The measures of central tendency of the percentage of aspiration-based sample losses were 15.19% (mean) and 11.66% (median), and of absorption-based sample losses were 23.91% (mean) and 15.92% (median). However, only 33.3% (3 of 9) of aspiration-based studies reported the number of sample losses against 81.8% (18 of 22) of absorption-based studies.
Meta-regression (meta-analysis) and random effects model investigated possible relationships between percentage of sample losses and the following variables at a significance level of 5%: collection method, collection material, collection time, and type of assay (Table 3). Aspiration resulted in fewer sample losses than absorption (p<0.0001).
| Variables | P-value | Effect Size |
|---|---|---|
| Collection Method   | <0.0001     | 0.1742 |
| Collection Material   | 0.2213 | 0.2385 |
| Type of Assay       | 0.0122 | 0.2163 |
| Collection Time     | 0.0632 | 0.123 |
Table 3. Evaluation of % loss according to the studied factors (type, material, essay and collection time) - Meta regression
The studies used the following assays to measure salivary cortisol: radioimmunoassay, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), liquid chromatographymass spectrometry, electrochemiluminescence and fluorescent immunoassay [6,8-14,34,36-39,41-57].
Inspection of the oral mucosa before saliva collection was one of the measures taken by the studies to avoid sample contamination with blood [46]. Three studies collected saliva 30 to 60 minutes after feeding to avoid sample contamination with milk [6,8,9,11,12,35,39,40,42,46- 48,57]. Two studies cleaned the oral cavity before saliva collection, and one study cleaned the oral cavity and collected a second saliva sample if the first sample appeared contaminated with blood [35,45,57]. Only one study did not exclude samples contaminated with blood or milk [2].
Discussion
The present review, which included studies published in the last ten years, aimed to help future studies by describing saliva collection methods, collection time, collection materials and the success rates of each method. The objective of most reviewed studies was to compare the level of stress in PTNs undergoing different therapies (Table 1). Salivary cortisol measurement may be a useful tool for assessing the cost-benefit ratio of some relaxation methods and the effects of stress caused by the NICU routine (heel lance, diaper change) [6,9,34,41].
The main objective of Ng et al. [45] was to describe a new methodology to collect PTNs’ saliva to measure cortisol. Although saliva collection is generally regarded as noninvasive, the local research ethics committee that approved said study considered suction invasive as it could injure PTN mucous membranes, which are extremely fragile, and contaminate the sample with blood. Another possible disadvantage of aspiration has to control suction pressure. None of the reviewed studies described the pressure parameters used. However, 9 of the 33 reviewed studies used aspiration, and none reported complications, such as mucosal injury during the procedure. On the other hand, two of the three studies that excluded samples contaminated with blood were aspiration based [8,11]. Unlike suction, the method described by Ng et al. [45] used swabs, which was well tolerated by PTNs as they did not demonstrate any sign of discomfort during collection. The authors found no adverse effects and 85% of the samples contained an adequate amount of saliva [46].
Absorbent material was the method of choice for saliva collection, used by 23 of the 33 reviewed studies. The materials included cotton buds, pediatric swabs or eye sponges of various brands [10,14,44,45]. The authors of two studies split the swab in four parts or in half, attaching it to a cotton bud to reduce its size and fit more comfortably in the PTNs’ mouths [2,49]. Other absorbent materials used by the studies were filter paper and sterile dental cotton rolls [13,55,56,57].
Morelius et al. [58] assessed plastic and wooden shaft swabs immediately after collection, 24 h after collection and 48 h after collection. Mean salivary cortisol was significantly lower in wooden shaft swabs 24 h (40%, p 0.001) and 48 h (49%, p 0.001) after collection than in wooden shaft swabs immediately after collection. However, the cortisol levels in samples collected with plastic shaft swabs did not differ. Hence, the authors recommend not to use both types of swabs in the same trial and to avoid using wooden shaft swabs as wood may absorb cortisol [59].
Twenty-one studies lost some samples due to insufficient saliva and/or blood contamination. Sometimes collecting an adequate amount of saliva is a challenge as the mucosa of some PTNs is extremely dry, especially in PTNs receiving anticholinergic agents, that is, mydriatic agents [42,53]. There is also loss caused by evaporation while the sample is frozen for storage or thawed for analysis [42].
Most studies used centrifugation to extract saliva from the absorbent materials. Such studies used Eppendorf® tubes or Salimetrics® tubes, which contain a separate compartment to store saliva and keep it separated from the absorbent material after centrifugation [2,10,41,42]. Ashwood et al. [56] used sterile dental cotton rolls to absorb saliva and then extracted the saliva by placing the roll inside a 5 ml syringe barrel and pressing the plunger top.
Inadequate saliva volume for the assay, the most common cause of sample loss, may be directly related to the type of assay chosen to measure cortisol as different assays require different amounts of sample. Studies that use assays that require smaller volumes are less likely to lose samples due to inadequate saliva volume. An advantage of using aspiration is the possibility of placing the saliva in a graduated container, which allows immediate awareness of the amount collected. Thus, collection time may be increased until the necessary amount is collected. On the other hand, saliva collected by absorbent materials can only be quantified after centrifugation or extraction by some other means, which is usually done some time after collection. None of the reviewed aspiration-based studies reported collection time while 68.2% (15 out of 22) of the absorption-based studies did (Table 2).
Some studies have not found an association between plasma and salivary cortisol levels, but other studies have [7,10,45,49,50]. Regardless of this correlation, salivary cortisol increases in individuals submitted to stressful situations [7]. Moreover, almost all studies reviewed herein managed to measure cortisol in at least part of the samples, regardless of saliva collection method, suggesting that this procedure is useful but not yet standardized.
Limitations
Although three databases were searched, this review may have missed studies compliant with the inclusion and exclusion criteria. The data in some reviewed studies may have been misinterpreted as they were not clear.
This review only included studies published in the last 10 years because collection materials have changed significantly and many studies were published during this period. Thus, earlier studies may contain important data not included herein.
Conclusion
Salivary cortisol measurement in preterm newborns may be useful for assessing and comparing the level of stress generated or relieved by different stimuli. Saliva collection methods have not been standardized, preventing the reproduction of studies that use these methods.
References
- Asadollahi M, Jabraeili M, Mahallei M, et al. Effects of gentle human touch and field massage on urine cortisol level in premature infants: A randomized, controlled clinical trial. J Caring Sci 2016; 5: 187-194.
- Schwilling D, Vogeser M, Kirchhoff F, et al. Live music reduces stress levels in very low birth weight infants. Acta Paediatr 2015; 104: 360-367.
- Ahmed RG, Suliman GI, Elfakey WA, et al. Effect of tactile kinesthetic stimulation on preterm infants' weight and length of hospital stay in Khartoum, Sudan. Saudi Med J 2015; 36: 196-199.
- Conde-Agudelo A, Diaz-Rossello JL. Kangaroo mother care to reduce morbidity and mortality in low birth weight infants. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2016; 8: Cd002771.
- Lyngstad LT, Tandberg BS, Storm H, et al. Does skin-to-skin contact reduce stress during diaper change in preterm infants? Early Hum Dev 2014; 90: 169-172.
- Morelius E, Hellstrom-Westas L, Carlén C, et al. Is a nappy change stressful to neonates? Early Hum Dev 2006; 82: 669-676.
- Calixto C, Martinez FE, Jorge SM, et al. Correlation between plasma and salivary cortisol levels in preterm infants. J Pediatr 2002; 140: 116-118.
- Soliman H, Elsharkawy A, Abdel-Hady H. Does topical lidocaine reduce the pain associated with the insertion of nasal continuous positive airway pressure prongs in preterm infants? A randomized, controlled pilot trial. Clin J Pain 2016; 32: 948-954.
- Castral TC, Warnock F, Dos Santos CB, et al. Maternal mood and concordant maternal and infant salivary cortisol during heel lance while in kangaroo care. Eur J Pain 2015; 19: 429-438.
- Moore TA, Schmid KK, French JA. Comparison of cortisol samples in the first two weeks of life in preterm infants. J Pediatr Endocr Met 2015; 28: 415-420.
- Osman M, Elsharkawy A, Abdel-Hady H. Assessment of pain during application of nasal-continuous positive airway pressure and heated, humidified high-flow nasal cannulae in preterm infants. J Perinatol 2015; 35: 263-267.
- Mitchell A, Chang J, Yates C, Hall RW. Challenges, guidelines, and systemic review of salivary cortisol research in preterm infants. e-Journal Neonatol Res 2012: 2.
- Maas C, Ringwald C, Weber K, et al. Relationship of salivary and plasma cortisol levels in preterm infants: results of a prospective observational study and systematic review of the literature. Neonatology 2014; 105: 312-318.
- Steen E, Bonamy AK, Norman M, et al. Preterm birth may be a larger risk factor for increased blood pressure than intrauterine growth restriction. Acta Paediatr 2015; 104: 1098-1103.
- Gover A, Brummelte S, Synnes AR, et al. Single course of antenatal steroids did not alter cortisol in preterm infants up to 18 months. Acta Paediatr 2012; 101: 604-608.
- Gover A, Chau V, Miller SP, et al. Prenatal and postnatal inflammation in relation to cortisol levels in preterm infants at 18 months corrected age. J Perinatol 2013; 33: 647-651.
- Mehler K, Ulbrich L, Borner S, et al. Multidimensional response to vaccination pain in very preterm, moderate- to late-preterm and full-term infants at age three months. Early Hum Dev 2015; 91: 199-204.
- Haley DW, Weinberg J, Grunau RE. Cortisol, contingency learning and memory in preterm and full-term infants. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2006; 31: 108-117.
- De Jong M, Cranendonk A, Van Weissenbruch MM. Salivary and serum cortisol and relation to blood pressure in infancy and early childhood in very low birth weight infants. Pediatr Res 2015; 78: 476-479.
- White-Traut RC, Schwertz D, McFarlin B, et al. Salivary cortisol and behavioral state responses of healthy newborn infants to tactile-only and multisensory interventions. J Obstet Gynecol Neonatal Nurs 2009; 38: 22-34.
- Nolan A, Lawrence C. A pilot study of a nursing Intervention protocol to minimize maternal-infant separation after cesarean birth. J Obstet Gynecol Neonatal Nurs 2009; 38: 430-442.
- Morelius E, Ortenstrand A, Theodorsson E, et al. A randomised trial of continuous skin-to-skin contact after preterm birth and the effects on salivary cortisol, parental stress, depression and breastfeeding. Early Hum Dev 2015; 91: 63-70.
- Róka A, Beko G, Halász J, et al. Changes in serum cytokine and cortisol levels in normothermic and hypothermic term neonates after perinatal asphyxia. Inflamm Res 2013; 62: 81-87.
- Aucott SW, Watterberg KL, Shaffer ML, et al. Early cortisol values and long-term outcomes in extremely low birth weight infants. J Perinatol 2010; 30: 484-488.
- Parga JJ, Harper RM, Karp H, et al. Low frequency rhythmic womb-like sounds modify autonomic activity in premature neonates. J Invest Med 2016; 64: 159-160.
- Hurrion EM, Harris M, Gray PG. Preterm-born children display altered hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis (HPAA) function and this is associated with infant temperament and 2 year cognitive and language scores. J Paediatr Child Health 2014; 50: 50-51.
- Ng SM, Turner M, Drury J, et al. Correlation of early morning plasma cortisol and salivary cortisol in extremely premature infants. Horm Res Paediat 2012; 78: 218.
- Van der Voorn B, de Waard M, van Goudoever JB, et al. Breast milk cortisol and cortisone concentrations follow the diurnal rhythm of maternal hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis activity. J Nutr 2016; 146: 2174-2179.
- Ak J, Lakshmanagowda PB, G CMP, et al. Impact of music therapy on breast milk secretion in mothers of premature newborns. J Clin Diagn Res 2015; 9: Cc04-6.
- Saatsaz S, Rezaei R, Sharifnia SH, et al. Effect of mother and newborn skin to skin contact on postpartum blues. J Babol Univ Med Sci 2011; 13: 60-65.
- Ludington-Hoe SM. Skin-to-skin contact: A comforting place with comfort food. Am J Matern Child Nurs 2015; 40: 359-366.
- Hochwald O, Holsti L, Osiovich H. Early testing for adrenal dysfunction in very low birth weight premature newborns. Paediatr Child Health 2011; 16: 7A-9A.
- Badiee Z, Nassiri Z, Armanian A. Co-bedding of twin premature infants: Calming effects on pain responses. Pediatr Neonatol 2014; 55: 262-268.
- Candia MF, Osaku EF, Leite MA, et al. Influence of prone positioning on premature newborn infant stress assessed by means of salivary cortisol measurement: pilot study. Rev Bras Ter Intensiva 2014; 26: 169-175.
- Badiee Z, Asghari M, Mohammadizadeh M. The calming effect of maternal breast milk odor on premature infants. Pediatr Neonatol 2013; 54: 322-325.
- Gibbins S, Stevens B, Beyene J, et al. Pain behaviours in Extremely Low Gestational Age infants. Early Hum Dev 2008; 84: 451-458.
- Ribeiro LM, Castral TC, Montanholi LL, et al. Human milk for neonatal pain relief during ophthalmoscopy. Rev Esc Enferm USP 2013; 47: 1039-1045.
- Cabral DM, Antonini SR, Custodio RJ, et al. Measurement of salivary cortisol as a marker of stress in newborns in a neonatal intensive care unit. Horm Res Paediatr 2013; 79: 373-378.
- Bauer J, Teufel U, Maser-Gluth C, et al. Effects of budesonide inhalation on energy expenditure, somatic growth and salivary cortisol levels in preterm infants with chronic lung disease. Horm Res 2009; 72: 146-152.
- Campbell-Yeo ML, Johnston CC, Joseph KS, et al. Co-bedding between preterm twins attenuates stress response after heel lance: Results of a randomized trial. Clin J Pain 2014; 30: 598-604.
- Dorn F, Wirth L, Gorbey S, et al. Influence of acoustic stimulation on the circadian and ultradian rhythm of premature infants. Chronobiol Int 2014; 31: 1062-1074.
- Klingenberg C, Pettersen M, Hansen EA, et al. Patient comfort during treatment with heated humidified high flow nasal cannulae versus nasal continuous positive airway pressure: A randomised cross-over trial. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 2014; 99: F134-137.
- Mitchell AJ, Yates CC, Williams DK, et al. Does daily kangaroo care provide sustained pain and stress relief in preterm infants? J Neonatal Perinatal Med 2013; 6: 45-52.
- Moore TA, Wilson ME, Schmid KK, et al. Relations between feeding intolerance and stress biomarkers in preterm infants. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2013; 57: 356-362.
- Ng SM, Drury JA, Turner MA, et al. A novel method of collection of saliva for estimation of steroid levels in extremely premature infants. Acta Paediatr 2013; 102: 356-359.
- Ivars K, Nelson N, Finnstrom O, et al. Nasopharyngeal suctioning does not produce a salivary cortisol reaction in preterm infants. Acta Paediatr 2012; 101: 1206-1210.
- Morelius E, Brostrom EB, Westrup B, et al. The Stockholm Neonatal Family-Centered Care Study: Effects on salivary cortisol in infants and their mothers. Early Hu Dev 2012; 88: 575-581.
- Chou IC, Lien HC, Lin HC, et al. The relationship of salivary and cord blood cortisol in preterm infants. J Pediatr Endocr Met 2011; 24: 85-88.
- Cong X, Ludington-Hoe SM, Walsh S. Randomized crossover trial of kangaroo care to reduce biobehavioral pain responses in preterm infants: a pilot study. Biol Res Nurs 2011; 13: 204-216.
- Cignacco E, Denhaerynck K, Nelle M, et al. Variability in pain response to a non-pharmacological intervention across repeated routine pain exposure in preterm infants: a feasibility study. Acta Paediatr 2009; 98: 842-846.
- Schaffer L, Luzi F, Burkhardt T, et al. Antenatal betamethasone administration alters stress physiology in healthy neonates. Obstet Gynecol 2009; 113: 1082-1088.
- Kleberg A, Warren I, Norman E, et al. Lower stress responses after newborn individualized developmental care and assessment program care during eye screening examinations for retinopathy of prematurity: A randomized study. Pediatrics 2008; 121: e1267-12678.
- Davis EP, Townsend EL, Gunnar MR, et al. Antenatal betamethasone treatment has a persisting influence on infant HPA axis regulation. J Perinatol 2006; 26: 147-153.
- Neu M, Hazel NA, Robinson J, et al. Effect of holding on co-regulation in preterm infants: A randomized controlled trial. Early Hum Dev 2014; 90: 141-147.
- Neu M, Laudenslager ML, Robinson J. Co-regulation in salivary cortisol during maternal holding of premature infants. Biol Res Nurs 2009; 10: 226-240.
- Ashwood PJ, Crowther CA, Willson KJ, et al. Neonatal adrenal function after repeat dose prenatal corticosteroids: A randomized controlled trial. Am J Obste Gynecol 2006; 194: 861-867.
- Castral TC, Warnock FF, Ribeiro LM, et al. Maternal factors regulating preterm infants' responses to pain and stress while in maternal kangaroo care. Rev Lat Am Enfermagem 2012; 20: 435-443.
- Morelius E, Nelson N, Theodorsson E. Saliva collection using cotton buds with wooden sticks: A note of caution. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 2006; 66: 15-18.
- Morelius E, He HG, Shorey S. Salivary cortisol reactivity in preterm infants in neonatal intensive care: An integrative review. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2016; 13: 1-5.